Table of Contents
Introduction
Operational Technology (OT) forms the backbone of critical infrastructure and industrial control systems, encompassing hardware and software that monitor and control physical devices and processes. From manufacturing plants and energy grids to water treatment facilities and transportation systems, OT plays a vital role in ensuring seamless industrial operations. As these systems increasingly connect to IT networks and the internet, they become vulnerable to cyber threats. In this landscape, threat detection emerges as a fundamental pillar of OT security.
Definition
Operational Technology (OT) Security refers to the practices, tools, and policies used to protect industrial control systems (ICS), supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, and other critical infrastructure that monitor and control physical processes. It focuses on safeguarding these systems from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and disruptions to ensure the safe, reliable, and continuous operation of essential services like energy, manufacturing, transportation, and water treatment.
Understanding OT Security and Threat Detection
Unlike Information Technology (IT), which primarily deals with data processing and communication, OT systems interact directly with the physical world, controlling machinery and processes in real time. Operational continuity is frequently given precedence over data confidentiality in OT contexts, where security is concerned with guaranteeing availability, safety, and integrity.
In OT security, threat detection is the process of locating possible cybersecurity threats, irregularities, and malevolent activity that might affect operational procedures. These threats may include malware, ransomware, insider sabotage, advanced persistent threats (APTs), or vulnerabilities stemming from legacy systems. With the convergence of IT and OT (often called IT/OT convergence), threat detection solutions must adapt to monitor both digital and physical domains.
The Role of Threat Detection in OT Security
Effective threat detection plays several critical roles in securing modern OT environments:
Early Identification of Anomalies:
OT systems typically have consistent patterns of operation. Threat detection tools monitor traffic and system behavior to flag any deviation from established norms, enabling early detection of cyber intrusions or insider threats.
Minimizing Downtime:
Threats like ransomware can bring industrial operations to a halt. By detecting these threats early, organizations can take proactive measures to isolate infected systems and maintain uptime—essential for industries like energy, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Protection of Critical Infrastructure:
The essential infrastructure of the country includes a lot of OT environments. Threat detection ensures these assets are safeguarded from nation-state actors, terrorist groups, or cybercriminals seeking to disrupt services or steal sensitive data.
Enabling Incident Response:
The process of incident response begins with detection. Accurate and timely alerts allow security teams to analyze, contain, and remediate threats before they escalate.
Compliance with Regulations:
Industries such as utilities and manufacturing are subject to strict cybersecurity regulations (e.g., NIST, NERC CIP, IEC 62443). Organisations can achieve these criteria and stay out of trouble legally and financially by putting threat detection into practice.
Key Benefits of Threat Detection in OT Environments
Deploying robust threat detection mechanisms in OT systems brings several significant benefits:
Improved Situational Awareness:
Threat detection tools provide a real-time view of the security landscape within an industrial network. This visibility helps operators understand what’s happening and react to threats more effectively.
Reduced Response Times:
Automated threat detection systems can immediately alert security teams to suspicious activity, significantly reducing the time it takes to respond to and mitigate threats.
Enhanced Network Segmentation:
Monitoring traffic between IT and OT networks allows organizations to detect and control unauthorized access attempts, supporting the implementation of segmentation and zero trust architecture.
Protection Against Insider Threats:
Not all security breaches come from the outside. Threat detection can identify unusual behavior from internal users or compromised accounts, helping to prevent sabotage or accidental disruptions.
Preservation of Safety and Reliability:
Cyberattacks in OT environments have the potential to cause environmental harm, fires, and equipment failures, among other safety risks. Risks to people, property, and the environment are reduced by early discovery.
Challenges in OT Threat Detection
While threat detection is crucial, implementing it in OT environments poses several unique challenges:
Legacy Systems:
Many OT systems are decades old and were never designed with cybersecurity in mind. These systems often lack logging or monitoring capabilities, making threat detection difficult.
Limited Downtime Windows:
Industrial systems are expected to run continuously, and updates or security implementations requiring downtime are often delayed or skipped, leaving vulnerabilities unaddressed.
Proprietary Protocols:
OT networks use a wide variety of vendor-specific and proprietary communication protocols, which can be difficult for standard cybersecurity tools to interpret.
Lack of Skilled Personnel:
There’s a shortage of professionals with expertise in both cybersecurity and OT systems. This skills gap makes it difficult to implement and manage advanced threat detection solutions effectively.
False Positives:
Small variations may result in alarms because OT systems are deterministic. Without proper tuning, threat detection systems may produce a high rate of false positives, leading to alert fatigue.
Future Trends in OT Threat Detection
As cyber threats evolve and industrial environments grow more complex, threat detection in OT security will continue to mature. The following trends will influence the future:
AI and Machine Learning Integration:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly used to detect subtle patterns and behaviors indicative of advanced threats. These technologies increase detection accuracy and decrease false positives.
Behavioral Analytics:
Instead of relying solely on known signatures, future detection tools will focus more on behavioral analytics to identify zero-day attacks and insider threats based on deviations from normal system behavior.
Edge-Based Detection:
With the rise of Industrial IoT (IIoT), edge computing will play a bigger role in threat detection. Monitoring at the edge allows faster response and reduces data sent to central systems, lowering latency and bandwidth consumption.
Unified Security Platforms:
There will be a push toward integrated platforms that bridge the gap between IT and OT security, offering centralized visibility and management across the entire infrastructure.
Threat Intelligence Sharing:
Collaborative threat intelligence frameworks will enable OT operators to share insights and indicators of compromise (IOCs) across industries, strengthening collective defense capabilities.
Regulatory Expansion:
Expect tighter regulations focused on OT cybersecurity. Governments and industry bodies will mandate the adoption of advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
Expansion Rate of Operational Technology (OT) Security Market
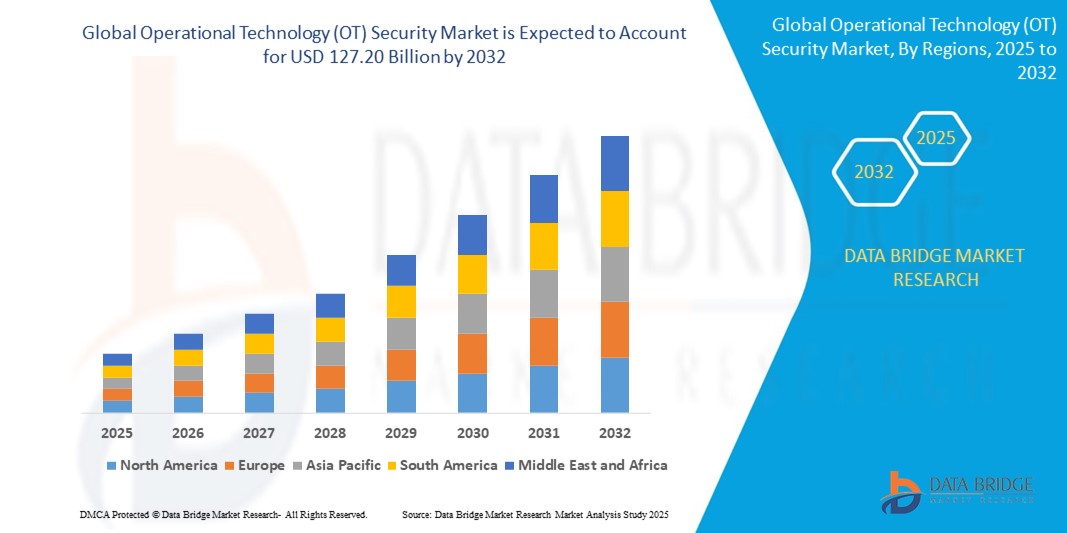
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global operational technology (OT) security market was estimated at USD 50.29 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.30% to reach USD 127.20 billion by 2032.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-operational-technology-ot-security-market
Conclusion
As OT environments become more connected and complex, they also become more susceptible to cyber threats. Threat detection is no longer optional – it is an essential component of modern OT security. It enables organizations to stay ahead of threats, protect critical infrastructure, and ensure the safety and continuity of industrial operations.